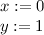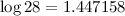Comment définir un nouvel opérateur ou symbole?
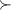 Il existe pour cela la commande
Il existe pour cela la commande \DeclareMathOperator du
package amsmath (explications sur AMS-TeX).
Elle s'utilise dans le préambule comme ici:
\documentclass{article} \usepackage{amsmath} \DeclareMathOperator{\init}{init} \begin{document} \[ \init f = 0 \mathrm{\ au \ lieu \ de~:} init f = 0 \] \end{document}
 On peut également utiliser
On peut également utiliser \newcommand, plutôt dans le préambule du document,
mais ce n'est pas obligatoire comme le montre cet exemple:
\newcommand{\affecte}{\mathrel{:=}} $x \affecte 0$ $y \affecte 1$
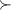 On peut utiliser
On peut utiliser \def comme ceci:
\makeatletter \def\log{\mathop{\operator@font log}\nolimits} \makeatother $\log 28 = 1.447158$
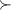 Pour définir un nouveau symbole de plusieurs caractères, il
faut utiliser la commande
Pour définir un nouveau symbole de plusieurs caractères, il
faut utiliser la commande \mathit.

![LaTeX
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\DeclareMathOperator{\init}{init}
\pagestyle{empty}
\begin{document}
\[
\init f = 0 \mathrm{\ au \ lieu \ de~:} init f = 0
\]
\end{document}](/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=wiki:latex:/img904fb0667b8914aab126dfe87b533479.png)